Specialized requirements – Getting Started with Edge Computing on AWS
Immersive experiences rely heavily on real-time user interactions, and any delay or lag can significantly degrade the user experience. AWS edge computing services can help to minimize latency by processing data closer to the source, thereby reducing the time taken to transmit data between the user’s device and the data center. Services such as AWS Wavelength and AWS Local Zones bring AWS services closer to end users, ensuring low-latency processing.
AR/VR applications often involve the transmission of large volumes of data, including high-resolution graphics, audio, and sensor inputs. This requires substantial network bandwidth to ensure seamless and immersive experiences. 5G devices are capable of as much as 10 Gbps of throughput in both directions – but generally only to the first hop. AWS Wavelength allows customers to capitalize on this fact by placing instances and containers directly at that first hop. Further, services such as AWS IoT Greengrass and AWS Snow Family enable local data processing and reduce the amount of data transmitted to the cloud in the first place.
As these applications grow in popularity and complexity, the underlying infrastructure must be able to scale accordingly. AWS provides scalable edge computing solutions that can adapt to the changing demands of AR/VR workloads, ensuring optimal performance and resource utilization. Finally, immersive experience applications often involve sensitive user data, making security a critical concern. AWS edge computing solutions incorporate robust security features, such as encryption, access control, and full auditability, to protect user data and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
IIoT
IIoT refers to the integration of internet-connected sensors, devices, and machinery in industrial settings. This includes manufacturing plants, utilities, oil and gas, transportation, and agriculture. IIoT leverages advanced technologies such as big data analytics, ML, and cloud computing to collect, analyze, and transmit data from various sources, allowing for real-time decision-making, process optimization, and improved operational efficiency. By connecting industrial assets and systems, IIoT enables organizations to monitor performance, predict and prevent equipment failures, and drive overall productivity and innovation within the industry.
Message Queuing Telemetry Transport
Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) is a lightweight, open source, and widely adopted messaging protocol designed for limited capacity networks, often used in Machine-to-Machine (M2M) and IoT applications where a low code footprint is required and/or network bandwidth is at a premium:
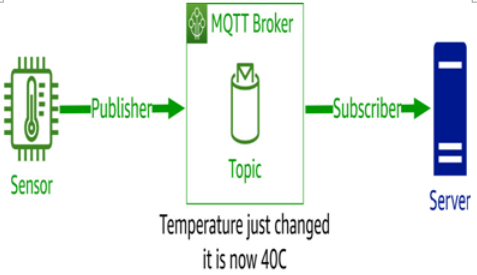
Figure 1.6 – MQTT’s publish/subscribe model
MQTT operates on a publish/subscribe model, which means that devices (clients) can publish messages to a topic on a central broker, and other devices can subscribe to the broker to receive these messages. This model allows for efficient data transfer and real-time updates, without requiring a continuous connection between devices.
MQTT is renowned for its efficient use of the network, ability to operate well in unreliable environments, and ease of implementation, making it an excellent choice for edge computing, mobile applications, and other scenarios where network conditions may be challenging.
Lastly, MQTT also supports a “last will and testament” feature that allows a client to publish a message when it disconnects ungracefully. This can be useful for monitoring and managing the status of devices.
By default, MQTT uses TCP ports 1183 (unsecured) and 8883 (TLS encrypted) for reliable transport over standard IP networks or the open internet. Most IIoT devices sold these days can natively use the MQTT protocol to communicate with brokers. However, this is not always the case.
You may also like
Archives
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- June 2021
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | ||||||
Leave a Reply