TCP RWIN FORMULA – Understanding Network and Security for Near-Edge Computing
Here’s the TCP RWIN formula:
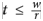
Here, we have the following:
t is the throughput in megabits per second
w is the RWIN in kilobits
r is the RTT value in milliseconds
When you’re trying to work out the effective throughput of any connection, both calculations must be performed. First, apply both the Mathis equation for packet loss, then apply the TCP RWIN formula. Whichever result is lower is the maximum throughput that connection will attain, regardless of the available bandwidth:
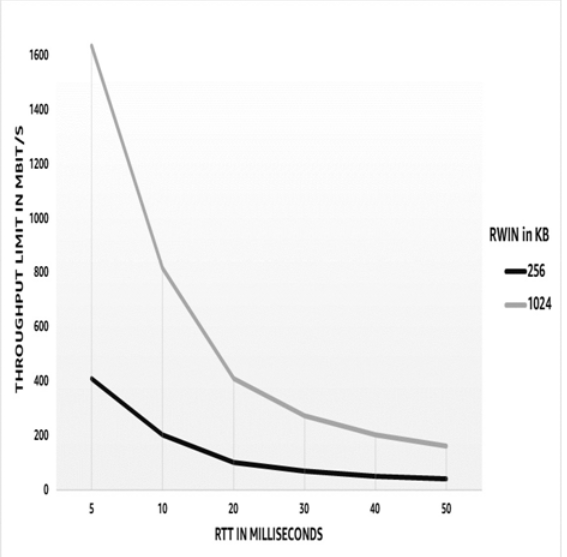
Figure 2.6 – Effective throughput estimated by the RWIN formula
Figure 2.6 demonstrates how the RWIN size conspires with higher RTTs to severely curtail maximum throughput. The lighter line on top shows an RWIN of 1,024 KB (or 1 MB), while the darker line represents an RWIN of 256 KB. TCP RWIN imposes hard limits on throughput in the same way that packet loss does.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
UDP is a common alternative to TCP that also operates at Layer 4 of the OSI model. Unlike TCP, UDP does not establish a connection – there is no three-way handshake. This means RTT and packet loss do not artificially limit the throughput a connection can achieve. One UDP stream is perfectly capable of filling the entire end-to-end bandwidth available to it.
The downside is that there is no error detection, no congestion control, no guarantee of delivery or ordering, and duplicate datagrams are not detected by it. This means the application needs to handle those things itself. Those are nontrivial things to implement per application. This is why applications that require reliable data transfer tend to rely on TCP to handle that for them.
However, there are applications for which reliable transmission doesn’t matter as much. Voice-over-IP (VOIP) applications such as Skype, WhatsApp, or FaceTime will just move on if some datagrams are lost. Online games such as Fortnite or Call of Duty use UDP because, again, once a datagram is lost, the real-time situation has moved on anyway. Applications such as YouTube, Netflix, and Hulu use UDP for their video streaming for that same reason.
Using a private wide-area network (WAN)
When the open internet proves too unreliable in terms of latency, jitter, packet loss, or path convergence, the historical answer has been for companies to build a private WAN using MPLS.
You may also like
Archives
- August 2024
- July 2024
- June 2024
- May 2024
- April 2024
- March 2024
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- July 2023
- May 2023
- April 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- June 2021
Calendar
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |||||
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 |
| 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | ||||||
Leave a Reply